Managing projects in Notion can feel overwhelming. With its endless customization options, it’s easy to get lost in setup rather than actually getting work done. You’re not alone if you’ve stared at a blank Notion page wondering how to transform it into a powerful project management system.
Here’s the good news: you don’t need to start from scratch. This guide provides both a free, ready-to-use template and a complete step-by-step tutorial to build your own Notion project management dashboard from the ground up. Whether you want to duplicate our template and start immediately or learn to build your own custom system, we’ve got you covered.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a centralized command center that tracks projects, tasks, deadlines, and team progress—all in one beautifully organized Notion workspace.
See It in Action: The Final Dashboard
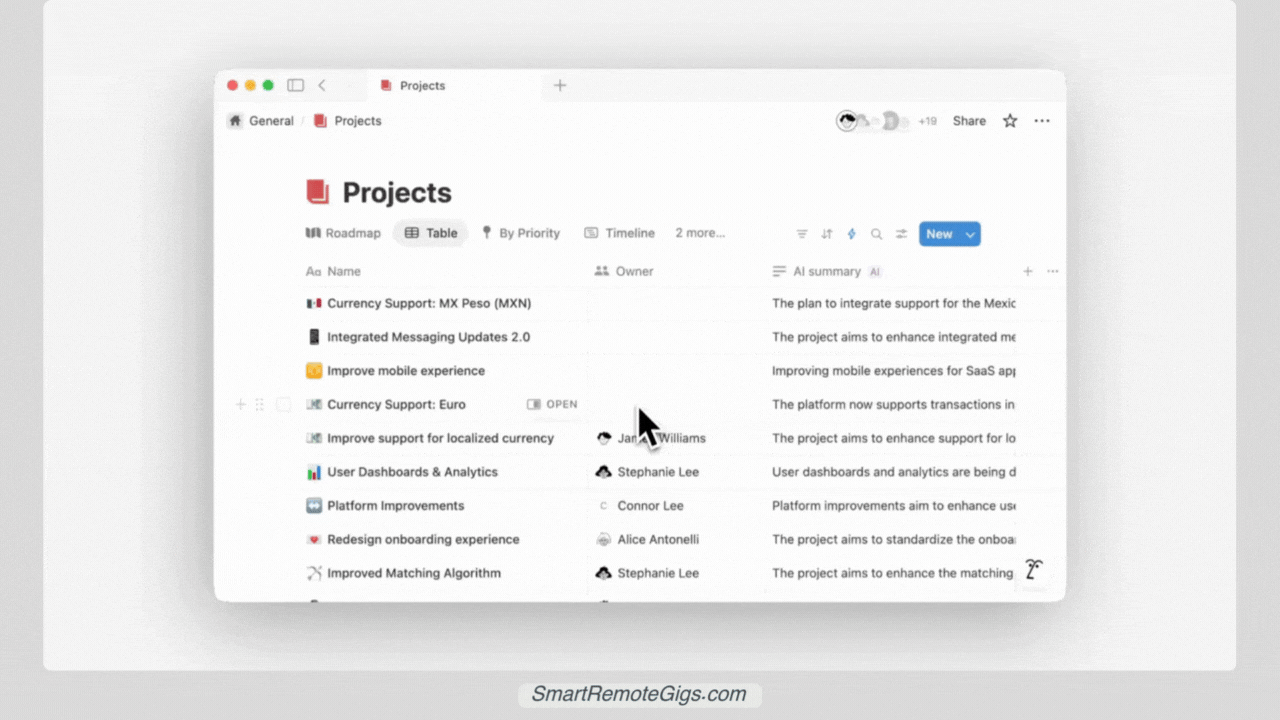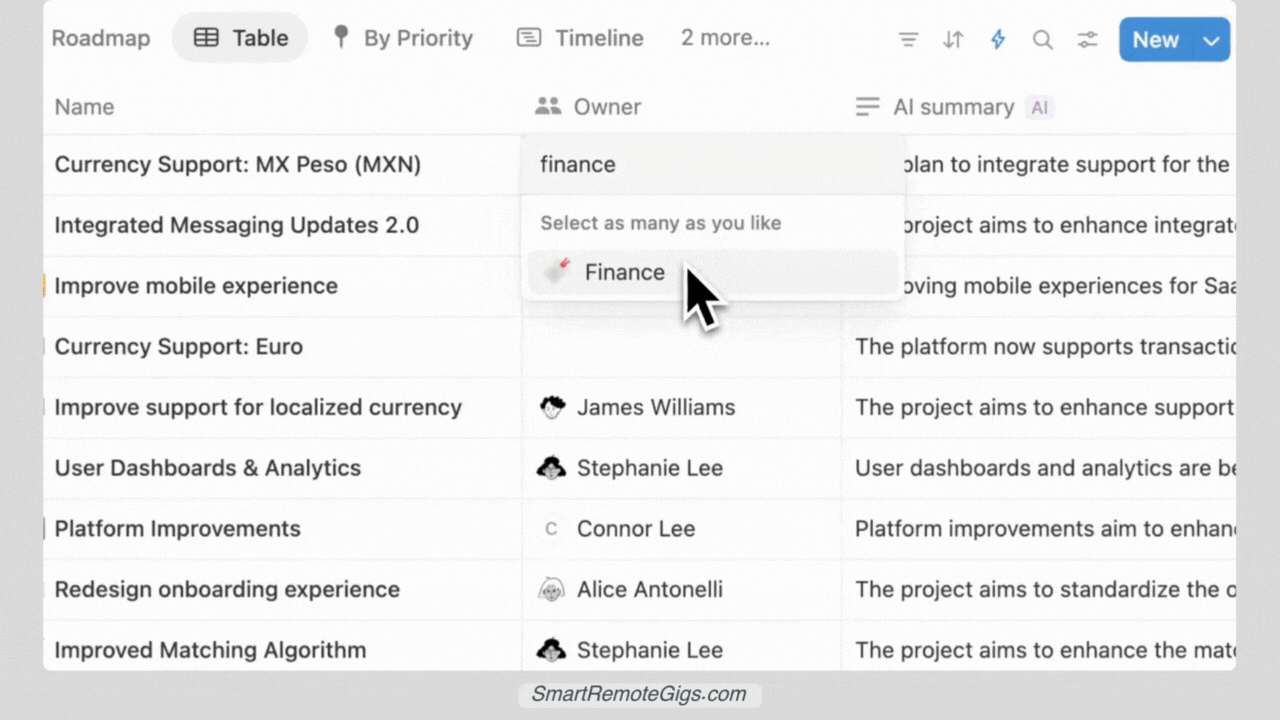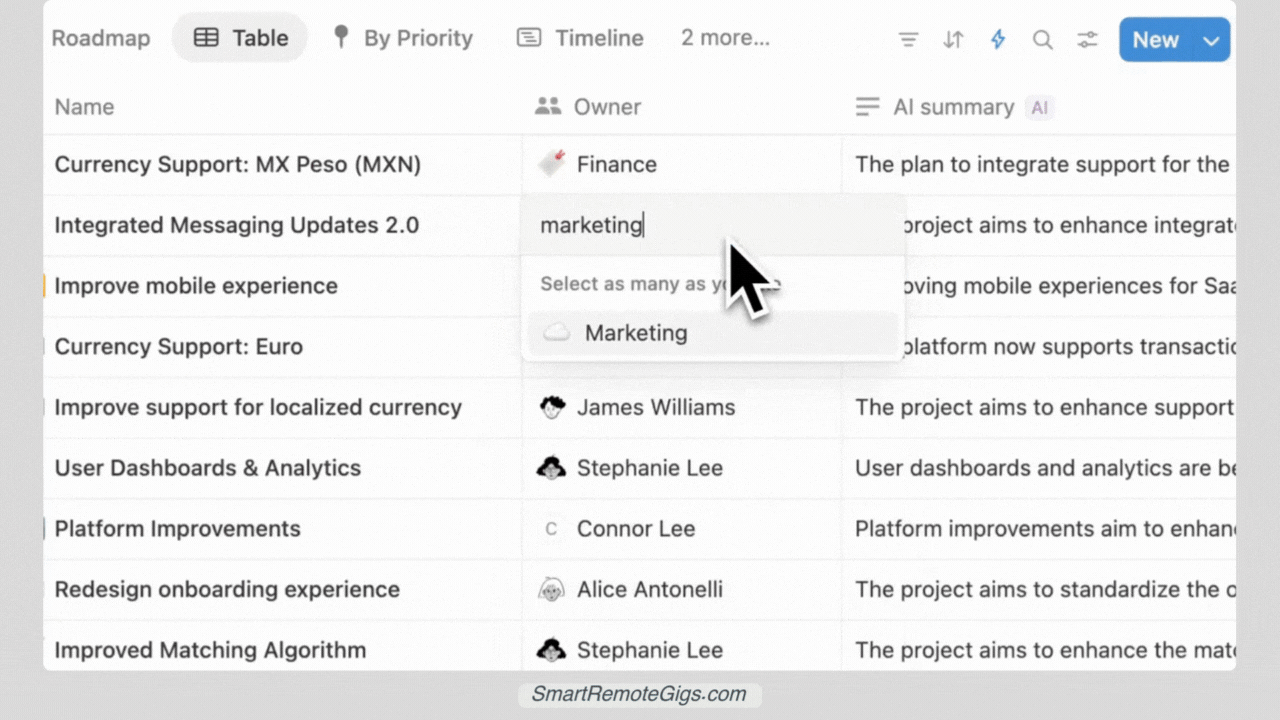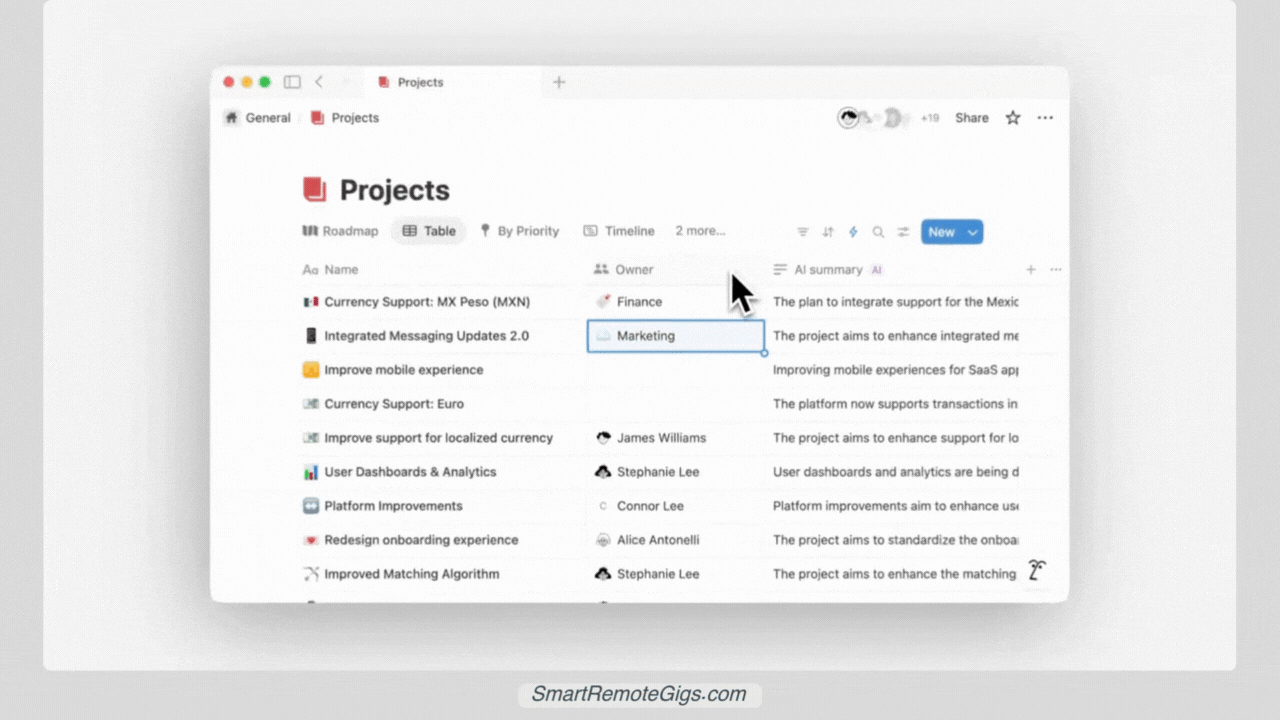
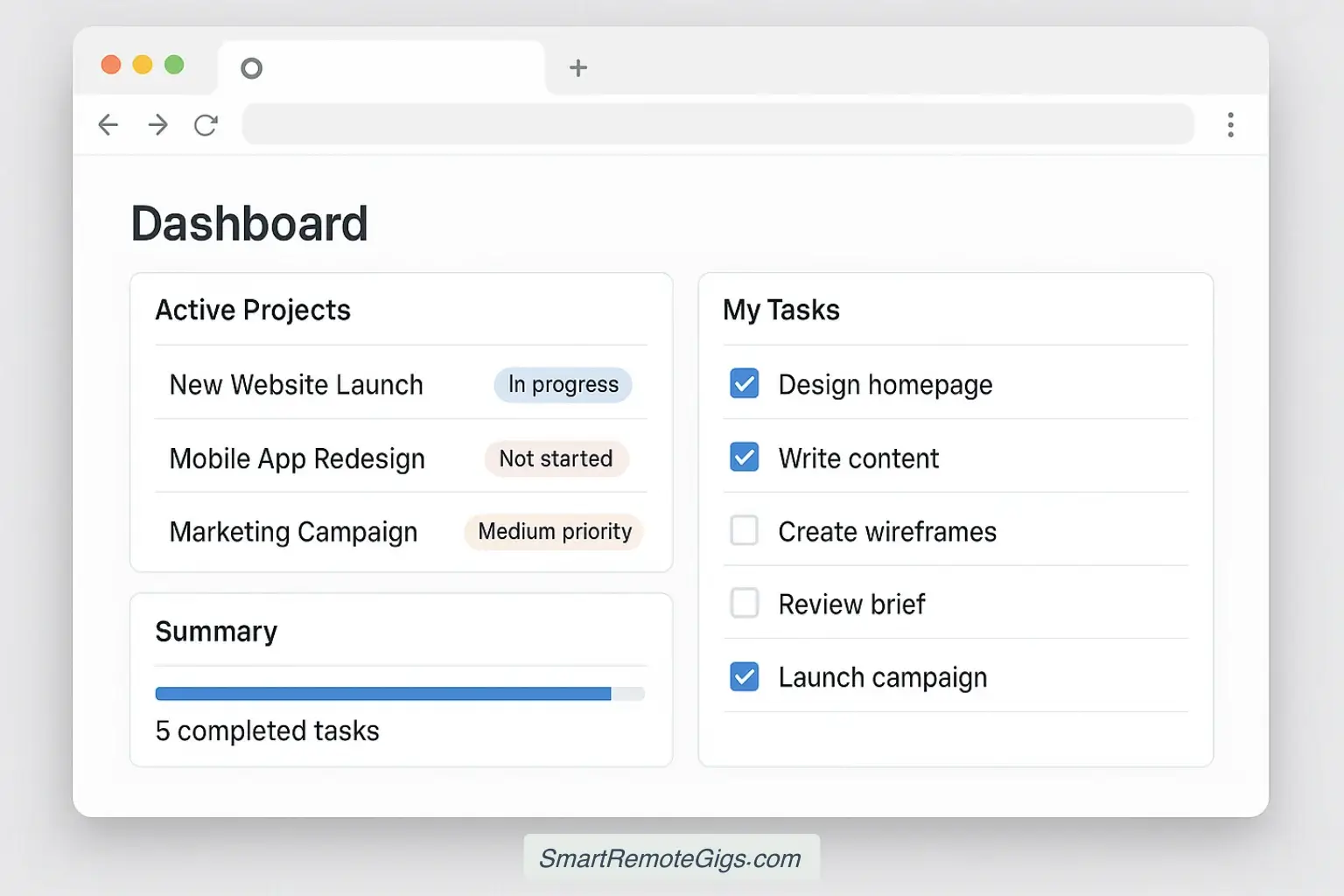
Before we dive into the build process, here’s what your finished dashboard will look like:
Key Features:
- Project Overview: See all active projects at a glance with status, timeline, and owner information
- Task Management: Kanban board, calendar view, and priority-based task lists
- Progress Tracking: Visual progress bars and completion percentages
- Team Collaboration: Assign tasks, set due dates, and track individual workloads
- Customizable Views: Filter by project, team member, priority, or deadline
The dashboard uses two connected databases (Projects and Tasks) that work together seamlessly, giving you both high-level project visibility and granular task management.
🎁 Get Your Free Project Management Template Now!
This template includes all databases, properties, views, and formulas pre-configured. Simply duplicate it to your workspace and start adding your projects immediately.
The Core Components: Understanding Our System
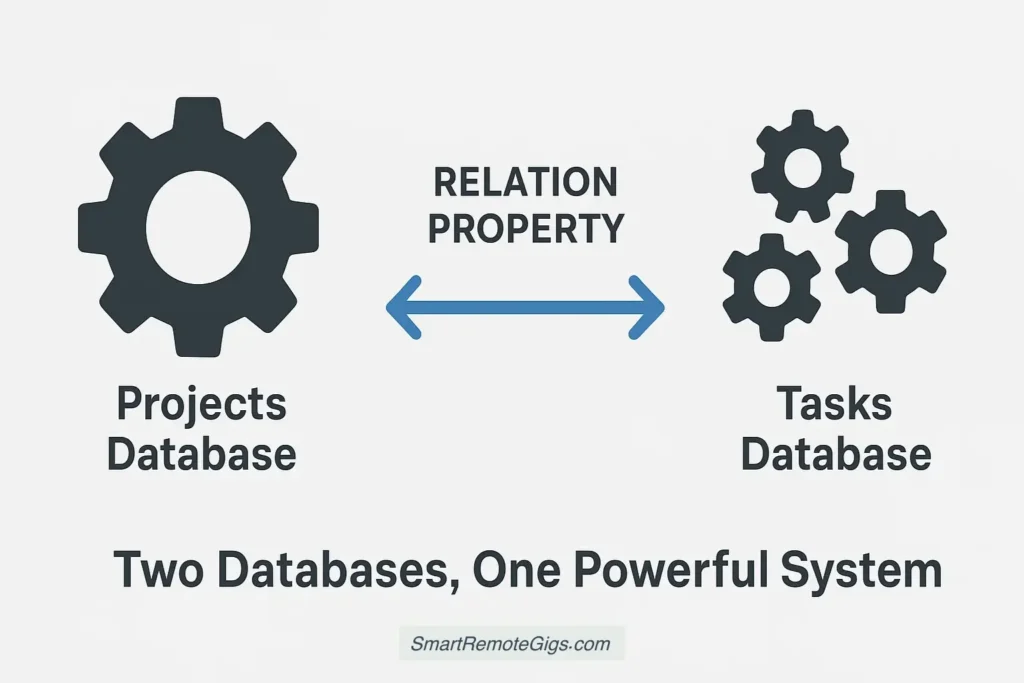
Our dashboard is built around a simple but powerful philosophy: two connected databases that talk to each other.
Projects Database: Your high-level view containing project names, status, timelines, budgets, and team assignments. Think of this as your “30,000-foot view.”
Tasks Database: The detailed work items that make up each project. Each task is linked to a parent project, creating a hierarchical structure that keeps everything organized.
The Magic Connection: Using Notion’s relation property, tasks automatically roll up to show project progress, while projects provide context for individual tasks. This bi-directional relationship ensures nothing falls through the cracks.
This system scales beautifully—whether you’re managing 3 projects or 30, the structure remains clean and navigable.
Step-by-Step: Building Your Dashboard from Scratch
Ready to build your own? Let’s create this system step-by-step. Each section includes detailed instructions and the exact settings you’ll need.
Step 1: Create Your “Projects” Database
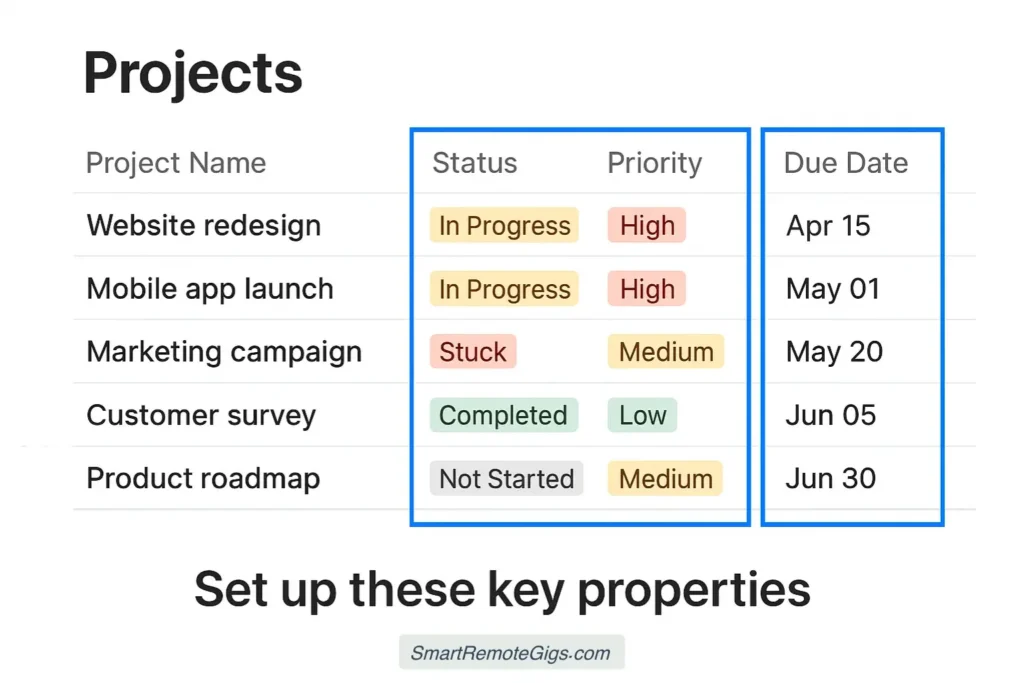
Start by creating a new page in your workspace and adding a database. Name it Projects and add these essential properties:
Essential Properties:
- Project Name (Title): The main identifier for each project
- Status (Select): Options include “Not Started,” “In Progress,” “On Hold,” “Completed,” “Cancelled”
- Priority (Select): “Low,” “Medium,” “High,” “Critical”
- Start Date (Date): When the project officially begins
- End Date (Date): Project deadline or completion target
- Project Owner (Person): The primary person responsible
- Budget (Number): Total project budget (optional)
- Description (Text): Brief project overview or goals
Advanced Properties:
- Progress (Formula): We’ll create this later to auto-calculate completion percentage
- Days Remaining (Formula): Auto-calculates time until deadline
- Task Count (Rollup): Total number of tasks (we’ll add this after creating the relation)
Setting Up Status Options:
For the Status property, use these specific options with color coding:
- Not Started (Gray)
- In Progress (Blue)
- On Hold (Yellow)
- Completed (Green)
- Cancelled (Red)
Step 2: Create Your “Tasks” Database
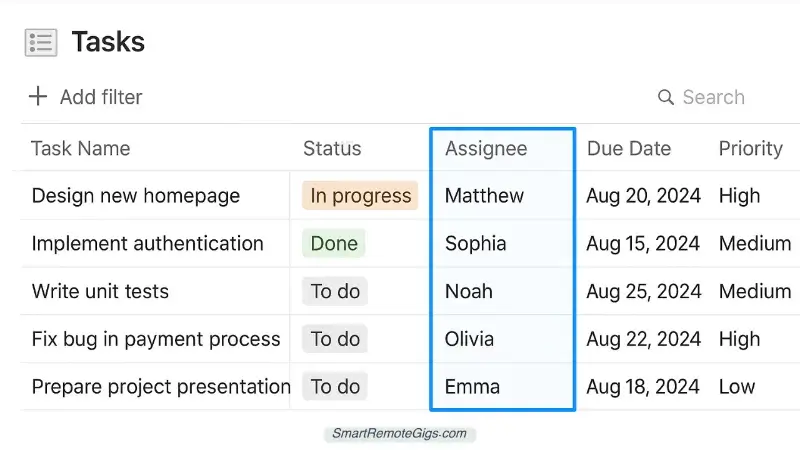
Create another database called Tasks with these properties:
Core Task Properties:
- Task Name (Title): Clear, actionable task description
- Status (Select): “Not Started,” “In Progress,” “Completed,” “Blocked”
- Priority (Select): “Low,” “Medium,” “High,” “Critical” (same as Projects)
- Due Date (Date): When the task must be completed
- Assignee (Person): Who’s responsible for this task
- Estimated Hours (Number): Time estimate for completion
- Actual Hours (Number): Time actually spent (filled in upon completion)
Organization Properties:
- Project (Relation): This will link to your Projects database—the key connection
- Tags (Multi-select): Flexible categorization (e.g., “Design,” “Development,” “Marketing”)
- Notes (Text): Additional context, links, or detailed instructions
Status Options for Tasks:
- Not Started (Gray)
- In Progress (Orange)
- Completed (Green)
- Blocked (Red)
Step 3: The Magic “Relation”: Linking Projects and Tasks
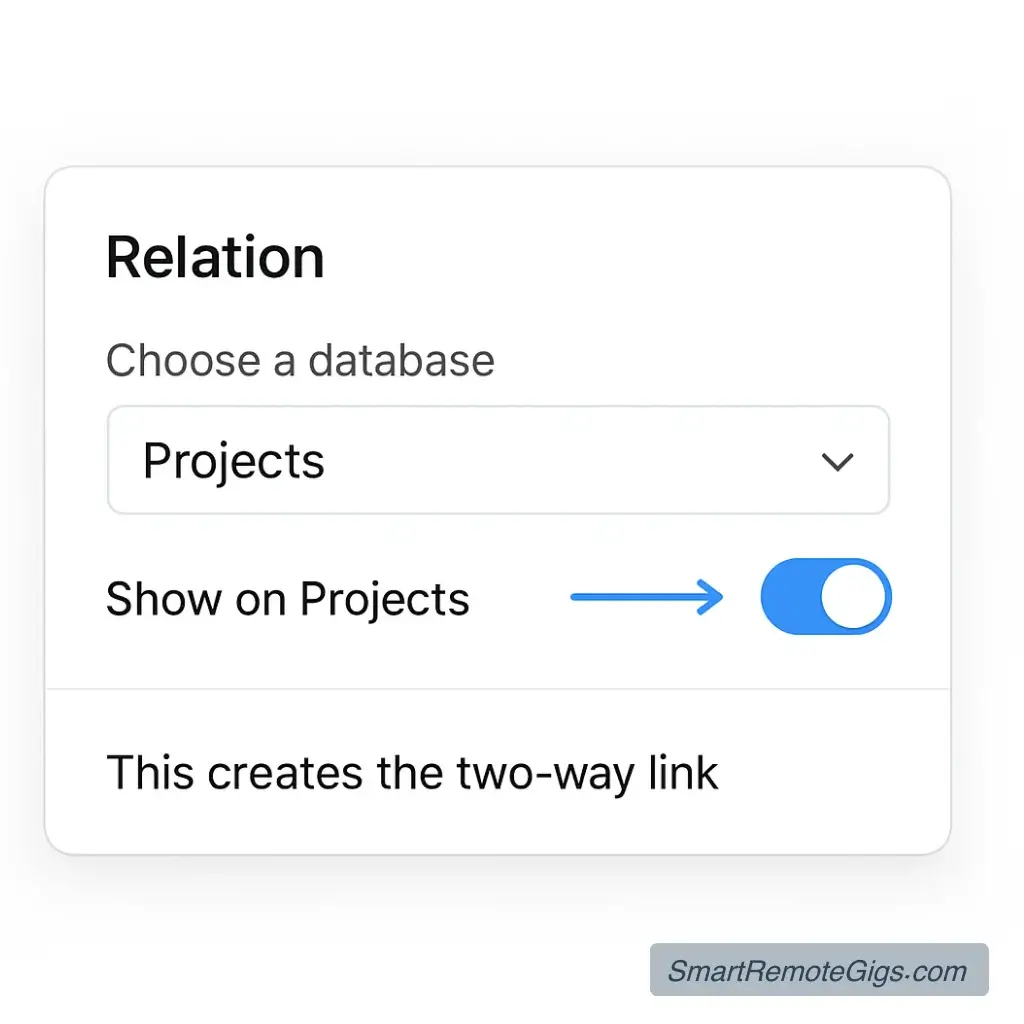
This is the most crucial step—creating the relationship between your databases:
In your Tasks database:
- Add a new property called Project
- Select “Relation” as the property type
- Choose your Projects database as the related database
- Check “Show on Projects” to create a two-way relationship
- Name the reverse property Tasks when prompted
What this accomplishes:
- Each task can be assigned to a specific project
- Each project automatically shows all its related tasks
- Progress can be calculated based on completed tasks
- Filtering and views work across both databases
Setting Up Rollup Properties:
In your Projects database, add these rollup properties to pull data from related tasks:
Task Count (Rollup):
- Relation: Tasks
- Property: Task Name
- Calculate: Count all
Completed Tasks (Rollup):
- Relation: Tasks
- Property: Status
- Calculate: Count values where Status equals “Completed”
Progress Formula:
Create a formula property called Progress with this formula:codeCode
if(prop("Task Count") > 0, round(prop("Completed Tasks") / prop("Task Count") * 100), 0)This automatically calculates completion percentage based on finished tasks.
Step 4: Building the Dashboard Page
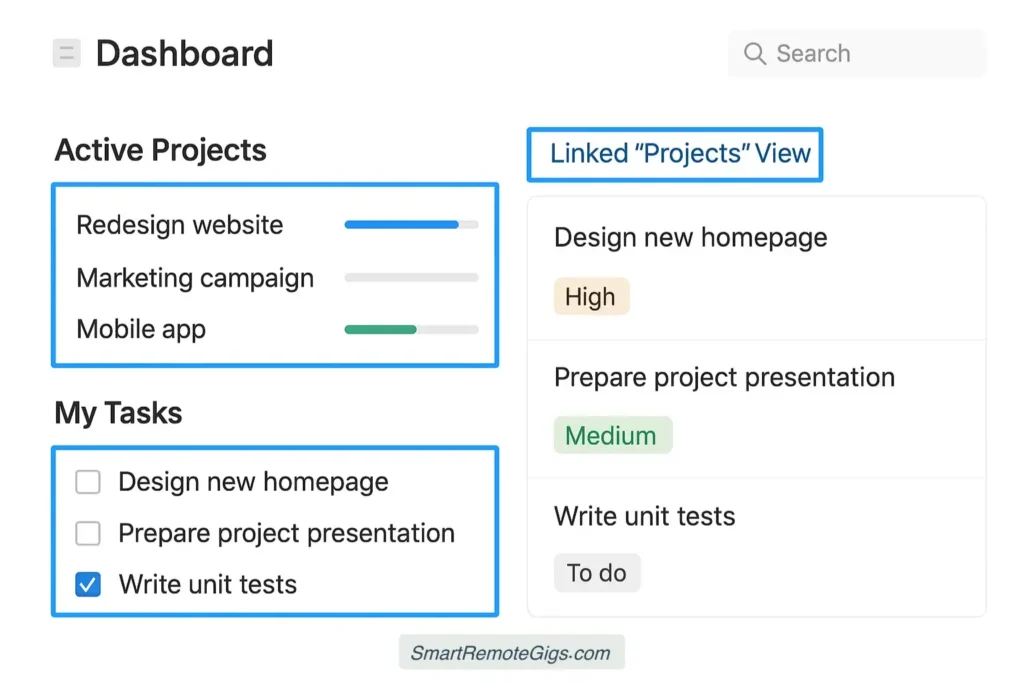
Create a new page called “Project Dashboard” and structure it like this:
Dashboard Layout:
Section 1: Quick Stats
Add a callout box with key metrics:
- Total Active Projects
- Tasks Due This Week
- Overdue Tasks
- Team Workload Summary
Section 2: Active Projects Overview
Add your Projects database as a linked view with these settings:
- View Type: Table
- Filter: Status is “In Progress”
- Sort: Priority (descending), then Due Date
- Visible Properties: Project Name, Status, Priority, End Date, Project Owner, Progress
Section 3: My Tasks (Current User)
Add your Tasks database filtered to show only tasks assigned to you:
- View Type: Table
- Filter: Assignee is “Current User” AND Status is not “Completed”
- Sort: Priority (descending), then Due Date
- Visible Properties: Task Name, Project, Priority, Due Date, Status
Section 4: Team Task Board
Add another view of your Tasks database:
- View Type: Board (Kanban)
- Group by: Status
- Filter: Show all active tasks
- Card Properties: Project, Assignee, Due Date, Priority
Step 5: Creating Useful Views (Kanban, Calendar, etc.)
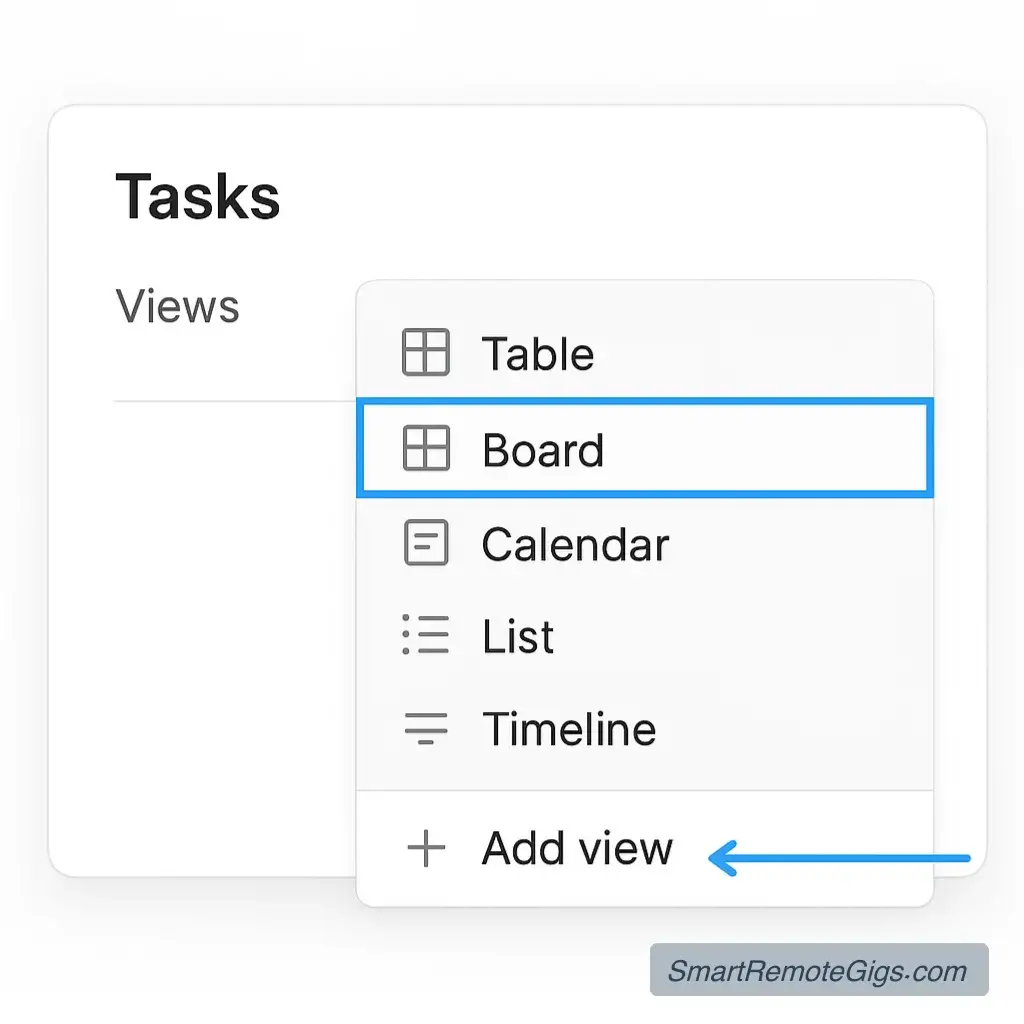
The power of Notion lies in creating multiple views of the same data. Here are essential views to set up:
For Projects Database:
1. Portfolio Overview (Table View)
- Shows all projects regardless of status
- Sorted by priority, then start date
- Includes all key properties for comprehensive overview
2. Active Projects Only (Table View)
- Filtered to exclude completed and cancelled projects
- Perfect for daily standup meetings and status updates
3. Timeline View (Timeline View)
- Group by Status
- Shows project duration and deadlines visually
- Excellent for resource planning and deadline management
For Tasks Database:
1. Kanban Board (Board View)
- Group by Status
- Shows workflow progression
- Easy drag-and-drop task management
2. Calendar View (Calendar View)
- Date property: Due Date
- Color-code by Priority or Project
- Perfect for deadline management and workload visualization
3. This Week (Table View)
- Filter: Due Date is within the next 7 days
- Sort: Due Date (ascending)
- Focus on immediate priorities
4. By Project (Table View)
- Group by Project
- Shows all tasks organized by their parent project
- Great for project-specific planning sessions
5. Overdue Tasks (Table View)
- Filter: Due Date is before today AND Status is not “Completed”
- Highlights missed deadlines that need immediate attention
How to Customize Your New Dashboard
Your dashboard is now functional, but here’s how to tailor it to your specific workflow:
Adding Custom Properties:
- Client Name: For agency work or consulting projects
- Revenue Impact: To prioritize high-value projects
- Risk Level: To flag projects that need extra attention
- Department: For larger organizations with multiple teams
Creating Team-Specific Views:
- Filter databases by team member or department
- Create separate dashboard pages for different teams
- Use templates for recurring project types
Integration Ideas:
- Link to Google Drive folders for each project
- Embed relevant documents or mockups
- Connect to time-tracking tools via Zapier
- Add links to GitHub repositories or design files
Advanced Formulas:
- Calculate project profitability (budget vs. actual costs)
- Auto-assign priority based on deadline proximity
- Create health scores based on multiple factors
- Generate automatic status updates based on task completion
Visual Enhancements:
- Add progress bars using Notion’s progress property
- Use icons and emojis for quick visual identification
- Create color-coded status indicators
- Add cover images for projects to improve visual recognition
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Relations Not Working: Ensure both databases are in the same workspace and the relation property is properly configured with “Show on [Database]” enabled.
Formulas Returning Errors: Check that property names in formulas exactly match your database properties (case-sensitive).
Views Not Updating: Refresh your browser or check filter settings—sometimes views need manual refresh after major changes.
Permissions Problems: Make sure team members have appropriate edit access to both databases if you’re collaborating.
Performance Issues: Large databases (1000+ items) may load slowly. Consider archiving completed projects to separate databases.
Best Practices for Long-Term Success
Consistent Data Entry: Establish clear naming conventions for projects and tasks. Use templates to ensure consistency across team members.
Regular Maintenance: Schedule weekly reviews to update project status, close completed tasks, and archive old projects.
Training Your Team: Create a simple onboarding guide showing team members how to add tasks, update status, and use different views.
Backup Strategy: Regularly export your databases or duplicate your workspace to prevent data loss.
Gradual Expansion: Start simple and add complexity gradually. Don’t overwhelm yourself or your team with too many properties initially.
Taking It Further: Advanced Features
Once you’re comfortable with the basic system, consider these advanced features:
Automated Workflows: Use Notion’s automation features (when available) or Zapier to automatically create tasks, send notifications, or update statuses.
Reporting Dashboard: Create a separate page with charts and metrics pulled from your project data using formulas and rollups.
Resource Management: Add properties to track team capacity, budget allocation, and resource conflicts.
Client Portal: Create filtered views that clients can access to see project progress without exposing sensitive internal information.
Template Gallery: Build project templates for common project types to speed up project creation and ensure consistency.
Conclusion: From Chaos to Control
You now have a powerful, scalable project management system that grows with your needs. This dashboard transforms Notion from a simple note-taking app into a comprehensive project command center that rivals expensive dedicated tools.
The beauty of this system lies in its flexibility—you can adapt it to any industry, team size, or project type. Whether you’re managing marketing campaigns, software development sprints, or creative projects, the core structure remains solid while allowing infinite customization.
Key Benefits You’ve Gained:
- Centralized Information: Everything related to your projects lives in one place
- Automated Progress Tracking: No more manual status updates or progress calculations
- Team Visibility: Everyone can see project status and their responsibilities
- Flexible Views: Multiple ways to slice and dice your project data
- Scalable Structure: Works for 3 projects or 300
Start by duplicating our free template, then gradually customize it to match your unique workflow. Remember, the best project management system is the one your team actually uses consistently.
Ready to get started? Grab the free template above, follow this guide, and transform your project management from chaotic to controlled in less than an hour.
For more ways to optimize your productivity workflow, explore our complete guide to the best note-taking apps and discover how the right tools can revolutionize your entire organizational system.
What projects will you tackle first with your new dashboard? The hardest part is often just getting started—now you have the tools to succeed.